Modern therapies
Now that the project to extend and upgrade the clinic is complete, staff and patients are benefiting not only from the extra space but also from modern technologies and treatment infrastructure. One of the important ways in which our services have been improved in Neurological Rehabilitation is by the use of modern, often robot-assisted therapies.
Erigo
Early mobilisation using a conventional tilt table is part of the standard therapy for neurological patients with severe sensorimotor impairment. The Erigo offers a unique new form of treatment because it combines gradually and slowly raising the patient into a standing position with robotic leg movement. This stimulates and stabilises the cardiovascular system during verticalisation so that patients are often better able to tolerate the upright position.
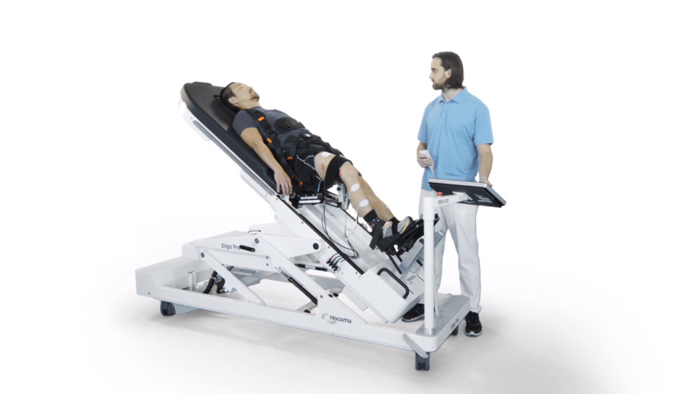
G-EO
The G-EO is a modern, robotic gait training system. Robot-assisted systems support gait rehabilitation very effectively thanks to the high number of repetitions and therefore the high number of steps taken. With the weight taken off the legs, walking, or certain aspects of walking, can be practised repetitively. This active form of treatment also enables the patient to play a conscious part in the therapy. It is a highly effective intervention for improving walking that works on the principle that: "If you want to learn to walk, you have to walk."
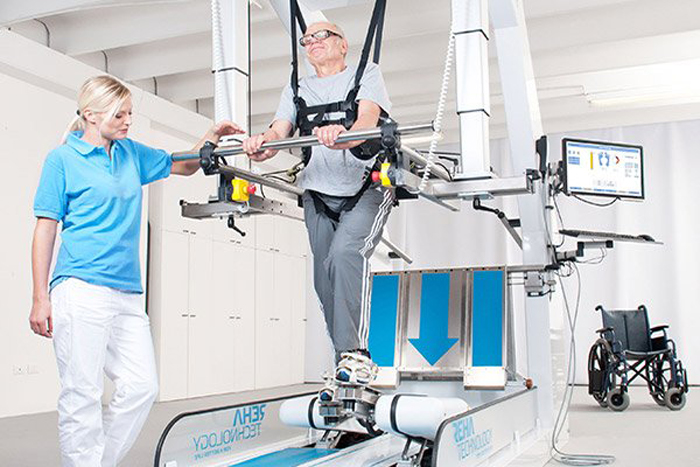

The FLOAT
The FLOAT is an innovative dynamic body weight support and guidance system for functional gait and balance training. The FLOAT allows unrestricted 360° movement and helps patients to train for everyday situations such as climbing stairs. The weight support system ensures that the patient is at no risk of falling and can feel confident in working to the best of their personal capabilities.

Andago
The Andago bridges the gap between gait training on a treadmill and walking freely. The dynamic body weight support system helps with gait and balance training so that patients can practise everyday situations with no risk of falling and can even move from room to room. The Andago does not have to be pulled or pushed but actively moves with the patient.

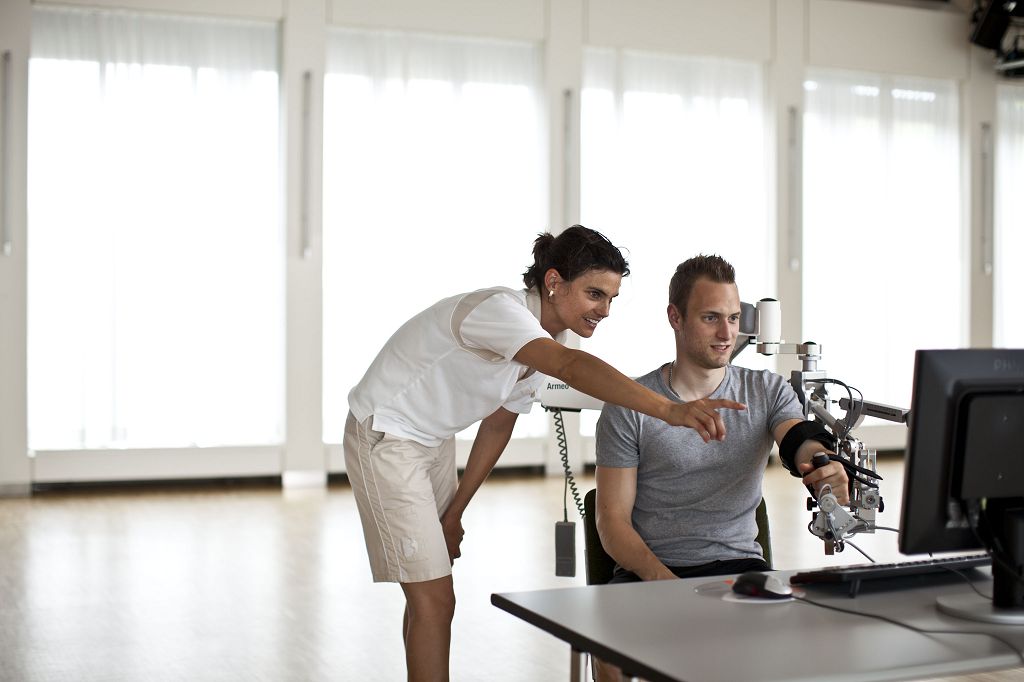
Armeo®Power
The Armeo®Power was developed for neurological patients with severe or complete paralysis of the arm. It is mainly used in the early stages of rehabilitation but is also suitable for the later stages. This robotic arm device is the world's first automated, self-moving exoskeleton for the arm that is available for use in hospitals. The exoskeleton is fitted with sensors and little motors for every direction of movement and actively offers the person doing the training exactly the amount of support that they need for a particular movement. On a screen, the patient sees virtual reality tasks that stimulate them to move their arm purposefully. The device provides direct feedback on the progress they have made during training.
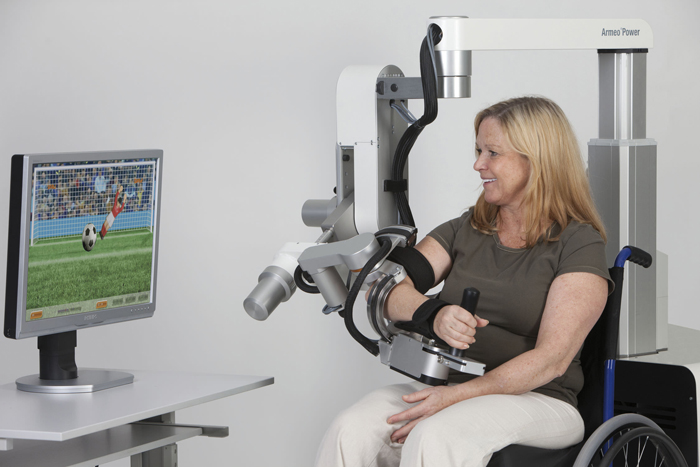
Armeo®Spring
The Armeo®Spring is used for neurological or orthopaedic patients who are already partly able to move their paralysed or injured arm themselves. The training is applicable in all stages of rehabilitation and is also used to encourage progress during chronic illness. The Armeo®Spring exoskeleton is a finely adjusted weight support system that counteracts gravity. Sensors detect the active moments made by the person doing the training. This means that self-initiated, customised and intensive training can be carried out in a large 3D space. Optionally, hand movements can be trained as well. The wide selection of virtual reality tasks offers plenty of variety and gives the patient direct feedback about their progress.

DIEGO
The DIEGO is suitable for neurological and orthopaedic patients who need finely adjusted weight support when exercising an arm that has been partially paralysed, injured or weakened in some way. The device can be used during all stages of rehabilitation. A robot-assisted system of slings provides intelligent weight relief so that exactly the right amount of support is given. It can be used to train one or both arms (uni- or bilateral training). Patients have the option of wearing a virtual reality headset to perform tasks on the screen. If the person wants to train using real, everyday objects on a table, the seat is simply rotated through 180°.

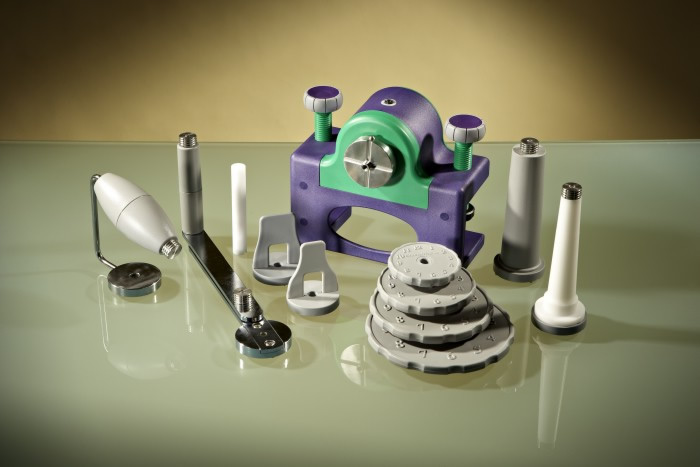
AMADEO
The AMADEO was developed for finger and hand rehabilitation during all stages of rehabilitation. Depending on the degree of neurological impairment or orthopaedic injury, the training can be carried out with the help of virtual reality tasks, in active, passive or assistive modes. The AMADEO can also be used to relieve spasticity and for sensory training. Biofeedback is used during training to show the level of performance and the progress that has been made.

Upper extremity therapy kit
The interactive, computer-based upper extremity therapy kit ("biometrics") offers a wide range of active exercises for orthopaedic and neurological patients, for the shoulder, elbow, lower arm or wrist or for individual fingers. The training exercises focus on strength, range of movement, coordination and speed of movement.

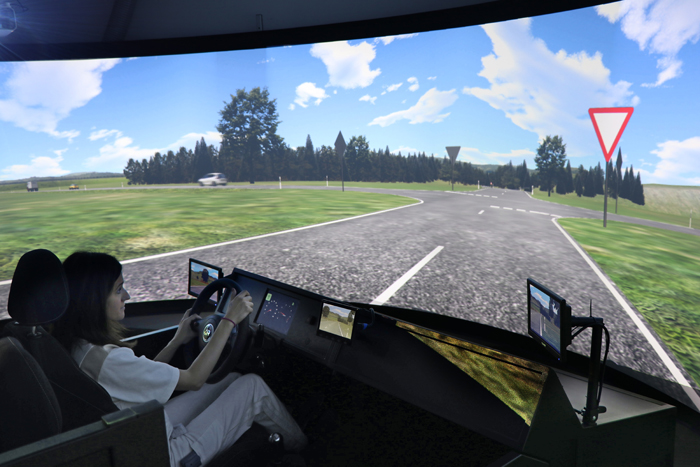
Driving simulator
The driving simulator can be used to assess the driving ability of our brain injury patients in standardised conditions that are as realistic as possible for different traffic scenarios (town, countryside, motorway). When taken together with their neurological and neuropsychological performance, the results help in assessing their suitability for driving a car. The simulator is also used for therapeutic purposes as a form of driver training.



